Abnormalities of the posterior segment are ideal
cases for B scan ultrasound. In the examination, the most commonly seen
B scans can be divided into four groups (remember that more than one
abnormality may be present):
a. abnormalities of the vitreous
b. abnormalities of the retina/choroid
c. tumours
d. optic disc drusen
e. miscellaneous conditions
a. Abnormalities of the vitreous:
-
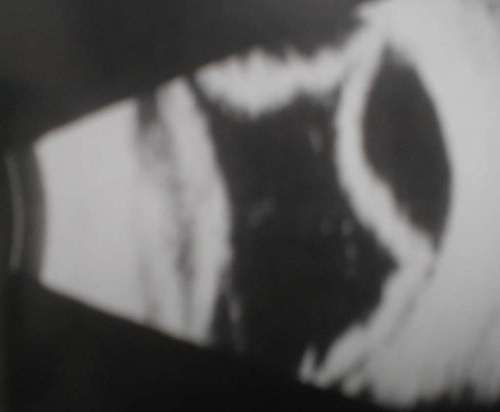
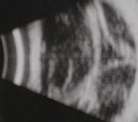
The scans usually show white opacities
within the vitreous cavity. The main differential
diagnosis being : vitreous haemorrhage,
asteroid hyalosis and synchysis scintillans.
-
The three may look similar on the ultrasound
but in the case of vitreous haemorrhage they
may be associated posterior vitreous
detachment or retinal tear.
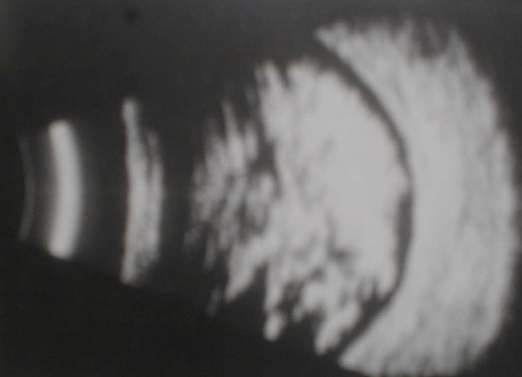
Figure 1a |
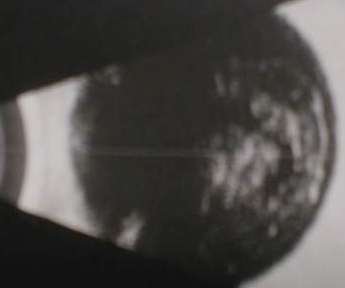
Figure 2a |
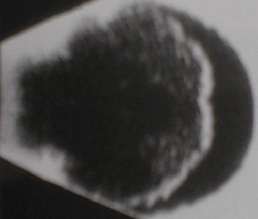
Figure 3a |
Of the three B scans above can
you differentiate asteroid hyalosis from vitreous haemorrhage?
|
|
|
|
b. Abnormalities of the retina/choroid
-
The scans usually show elevated lesions projecting into the
vitreous cavity.
-
The main differential diagnosis is between retinal detachment
and choroidal detachment.
-
In the case of choroidal detachment, the elevation is dome-shaped
and has a smooth outline. On the other hand, retinal detachment has an
irregular surface.
-
Additional abnormalities to look for are:
-
fluid level (especially in choroidal detachment)
-
vitreous haemorrhage
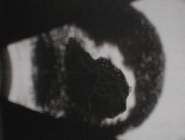
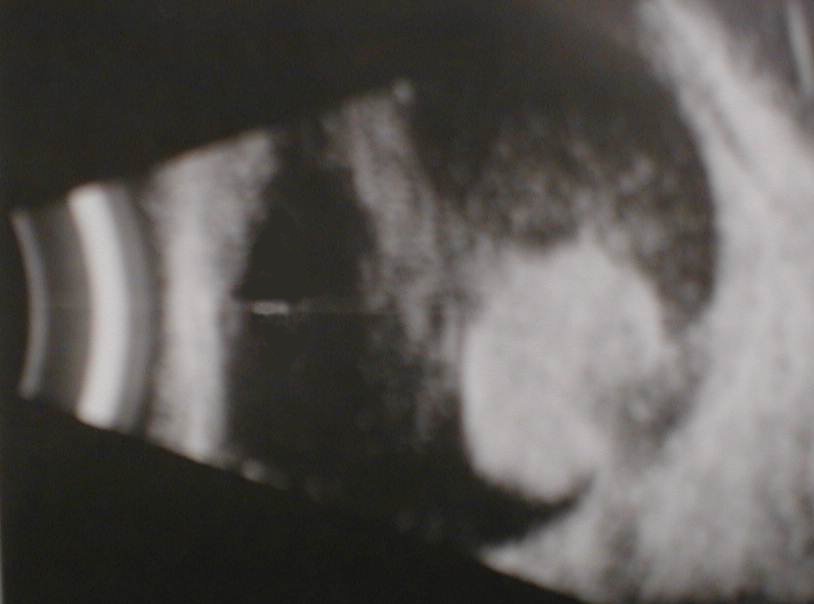
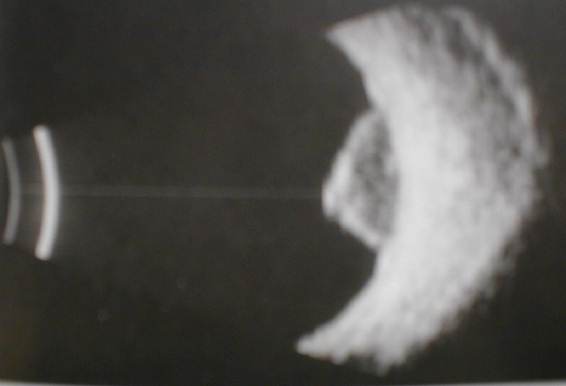
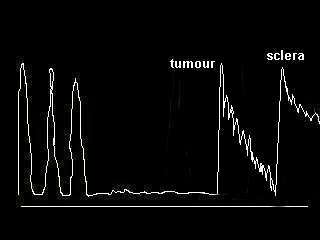
c. Tumours
-
The most likely tumour is choroidal melanoma. Occasionally
you may be given retinoblastoma, the age is a clue.
-
In choroidal melanoma, look for excavation, associated choroidal
or retinal detachment and scleral invasion.
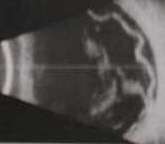
d. Optic disc drusen
-
If the ultrasound shows normal vitreous and absence of retinal
or choroidal abnormalities, look for the presence of bright white area
in the optic disc ie. drusen (See picture below).
-
Although ultrasound has been used to detect papilloedema
and glaucomatous optic disc, you are unlikely to be given such cases in
OSE.
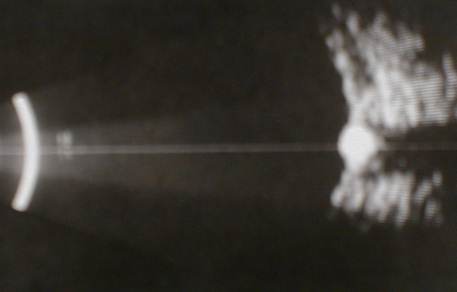
Figure 4a |
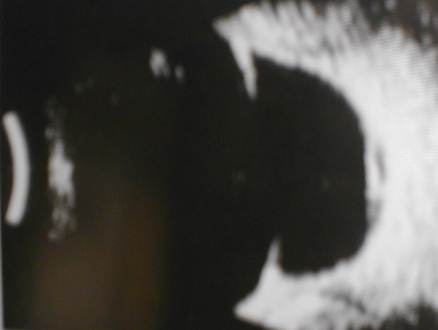
e. Miscellaneous conditions
-
a-b cover the most common cases seen in the OSE. The following
scans have yet to appear in the OSE, could you diagnose the abnormalities
?
( In the OSE you can not ask for the clinical findings
but if any of the scans were to appear in the viva section of the
final MRCOphth, always tell the examiners that you like to see the colour
picture or perform a clinical examination. Like all imagings, the ultrasounds
only supplement the clinical findings)
 |
This patient has significant
difference in axial lengths between the two eyes. What does this scan show?
|
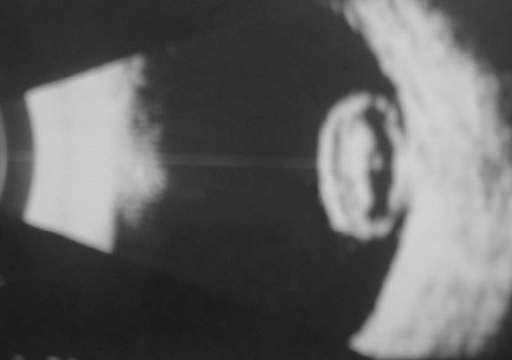 |
This patient requires high plus
lens for good vision. What does the scan show?
|
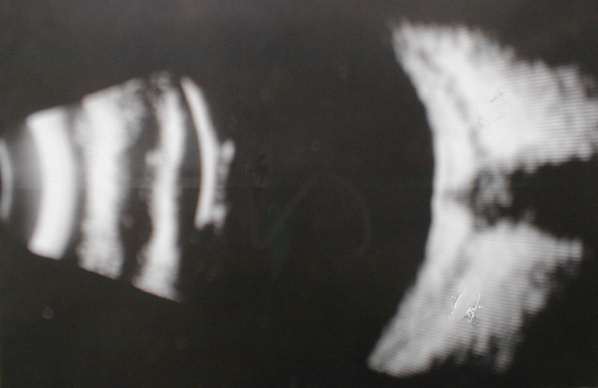 |
This patient has a painful eye.
What does the scan show?
|
|